Meaning of Tissue
Tissue
A tissue is a group of similar cells that work together to perform one specific function efficiently.
Can you name a tissue you see every day?
Plants vs Animals
Plant Tissues
Animal Tissues
Key Similarities
Where Growth Happens
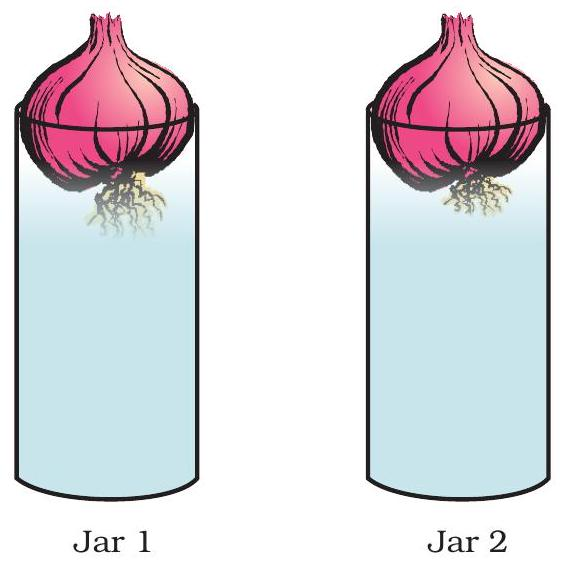
Onion-root experiment: Jar 1 intact tips vs Jar 2 cut tips
Onion-root activity
Jar 1 keeps elongating because its root tips are untouched.
Jar 2 stops growing when tips are removed—its growth zone is gone.
Key Points:
- Meristematic tissue sits at root tips.
- It rapidly makes new cells, adding length.
- Cutting the tip removes meristem, so growth stops.
Meristem Types
Meristematic Tissue
Meristematic tissue is a set of living cells that continuously divide to create new plant organs.
Key Characteristics:
- Apical meristem – adds length at root and shoot tips.
- Intercalary meristem – extends internodes at nodes or leaf bases.
- Lateral meristem – thickens stems and roots.
Spot the Meristems
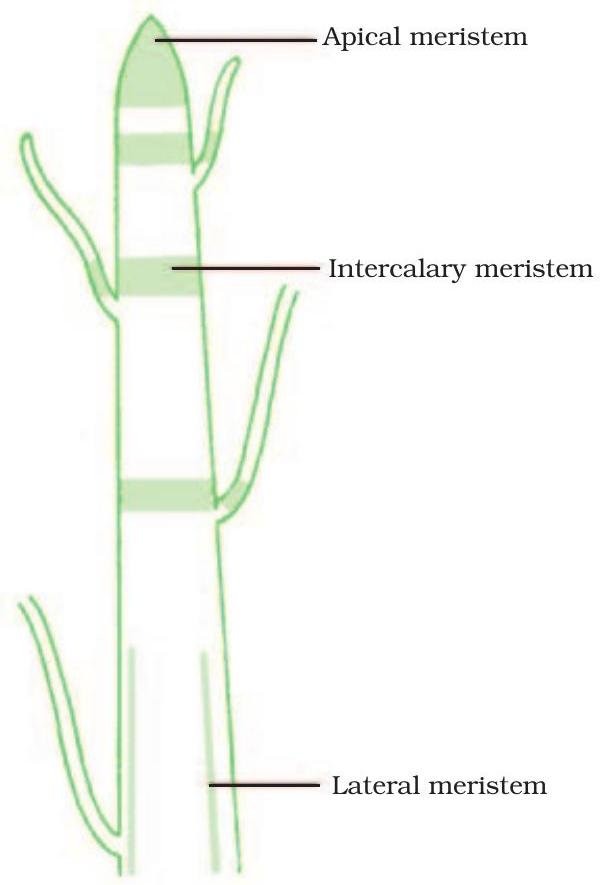
Stem diagram with labelled growth zones
Can you locate each growth zone?
Read the diagram carefully. Three tiny meristem areas control length and thickness of the plant.
Key Points:
- Apical – at very tip; makes stem or root longer.
- Intercalary – near node/internode; lengthens region between leaves.
- Lateral – side layers; increases stem thickness.
Simple Tissues Trio
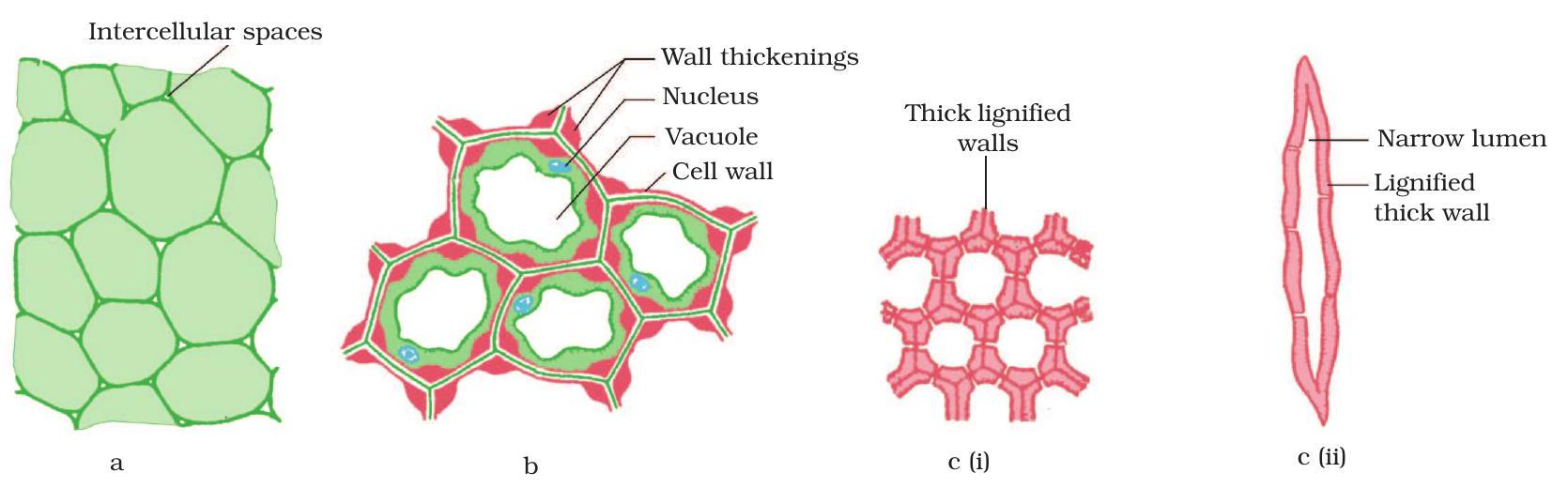
Simple Permanent Tissues
These tissues have similar cells and perform basic storage or support roles in plants.
Key Points:
- Parenchyma – soft, living cells; stores food and water.
- Collenchyma – uneven cell walls; flexible support for growing stems.
- Sclerenchyma – thick, dead walls; very hard, adds strength (coconut husk).
Match Tissue to Role
Drag each tissue to the plant function it performs. Test your memory through active recall.
Draggable Items
Drop Zones
Stores food
Adds flexibility
Provides hardness
Makes plant longer
Tip:
Remember: meristems drive growth, while mature tissues mainly support or store.
Results
Key Takeaways
Tissues in a nutshell
What is a tissue?
A tissue is a group of similar cells working together for one function.
Two main kinds
Plant tissues are meristematic (dividing) or permanent (mature & specialised).
Meristematic zones
Found at root, shoot, and cambium; they drive length and thickness growth.
Permanent details
Simple: parenchyma, collenchyma, sclerenchyma. Complex: xylem & phloem.