Parts of a Polynomial
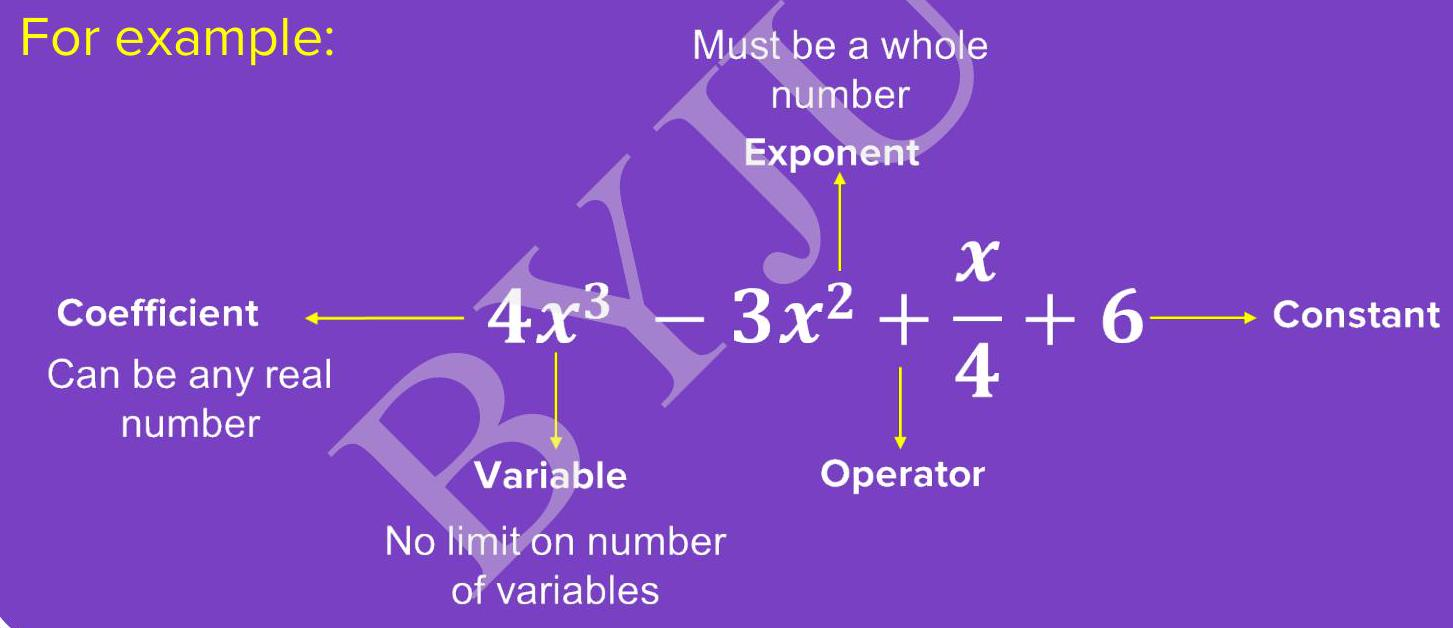
Pattern in every term
Each arrow shows one part. Every term fits: coefficient × variable\(^{\text{exponent}}\).
Key Points:
- Coefficient – number multiplied by the variable.
- Variable – letter that can change value.
- Exponent – small power on the variable.
- Operator – + or – sign joining terms.
- Constant – term without a variable.
What is a Polynomial?
Polynomial
A polynomial in one variable is a sum or difference of terms \(a x^{n}\) where \(a\) is any real number and \(n\) is a whole number \(0,1,2,\dots\).
1, 2, or 3 Terms?
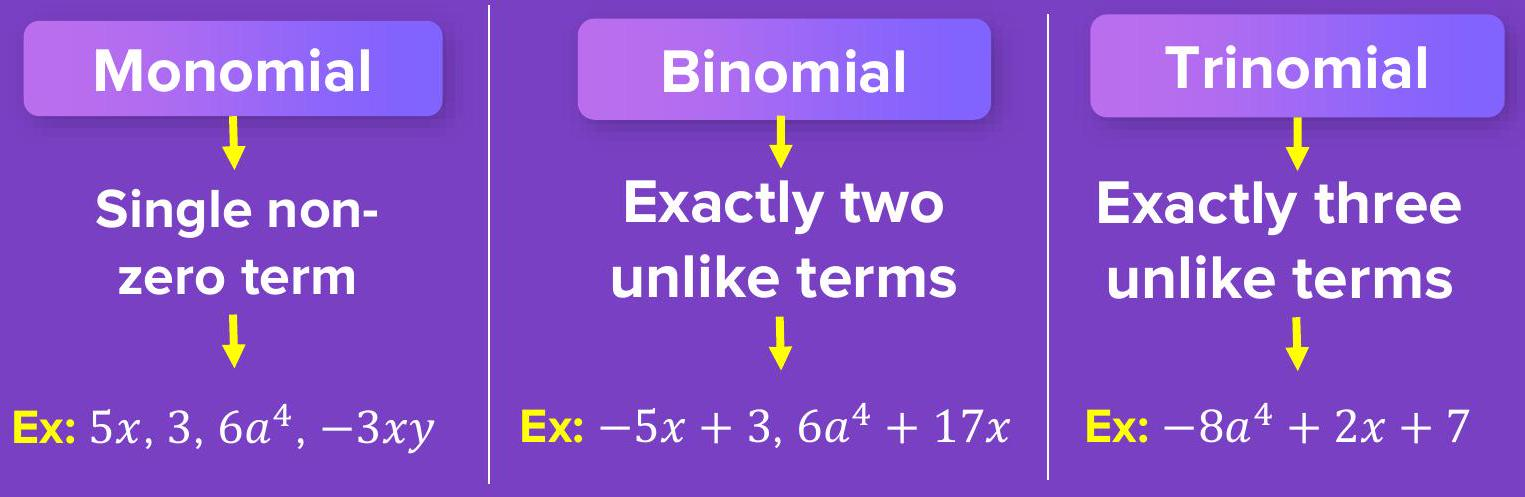
Types by Number of Terms
Count the unlike terms in an expression to name it correctly.
Key Points:
- Monomial → 1 term, e.g. \(5x\)
- Binomial → 2 terms, e.g. \(3x+2\)
- Trinomial → 3 terms, e.g. \(x^{2}+2x+1\)
Sort the Expressions
Drag each algebraic expression into its correct basket: monomial, binomial, or trinomial.
Draggable Items
Drop Zones
Monomial
Binomial
Trinomial
Tip:
Count unlike terms: 1 → monomial, 2 → binomial, 3 → trinomial.
Results
Degree of a Polynomial
Degree
The degree is the highest power (largest exponent) of the variable in a polynomial.
Key Characteristics:
- Highest power decides the degree.
- Degree 1 → Linear polynomial.
- Degree 2 → Quadratic polynomial.
- Degree 3 → Cubic polynomial.
Example:
\(5x^2 + 3x + 1\) has highest exponent \(2\); therefore, it is quadratic.
Check Your Pick
Question
Formative assessment: Which expression below is NOT a polynomial in \(x\)?
Hint:
A polynomial has only whole-number exponents on \(x\).
Correct!
Yes—\(x^{-1}+2\) contains a negative exponent, so it is not a polynomial.
Incorrect
Remember: every exponent in a polynomial must be a non-negative integer.
Key Takeaways
A polynomial is a sum of terms \(a x^{n}\) where \(n\) is a whole number.
Each term has a coefficient, variable, exponent, and sometimes a constant part.
By term count, we label them monomial, binomial, or trinomial.
The highest exponent, called degree, classifies polynomials as linear, quadratic, or cubic.
Thank You!
We hope you found this lesson informative and engaging.