What Is a Polynomial?
Polynomial
A polynomial is an algebraic expression with terms added or subtracted. Each term equals a coefficient multiplied by the variable raised to a whole-number exponent.
Can you spot the coefficient, variable, and exponent in \(3x^{2}+2x-5\)?
Parts of a Polynomial
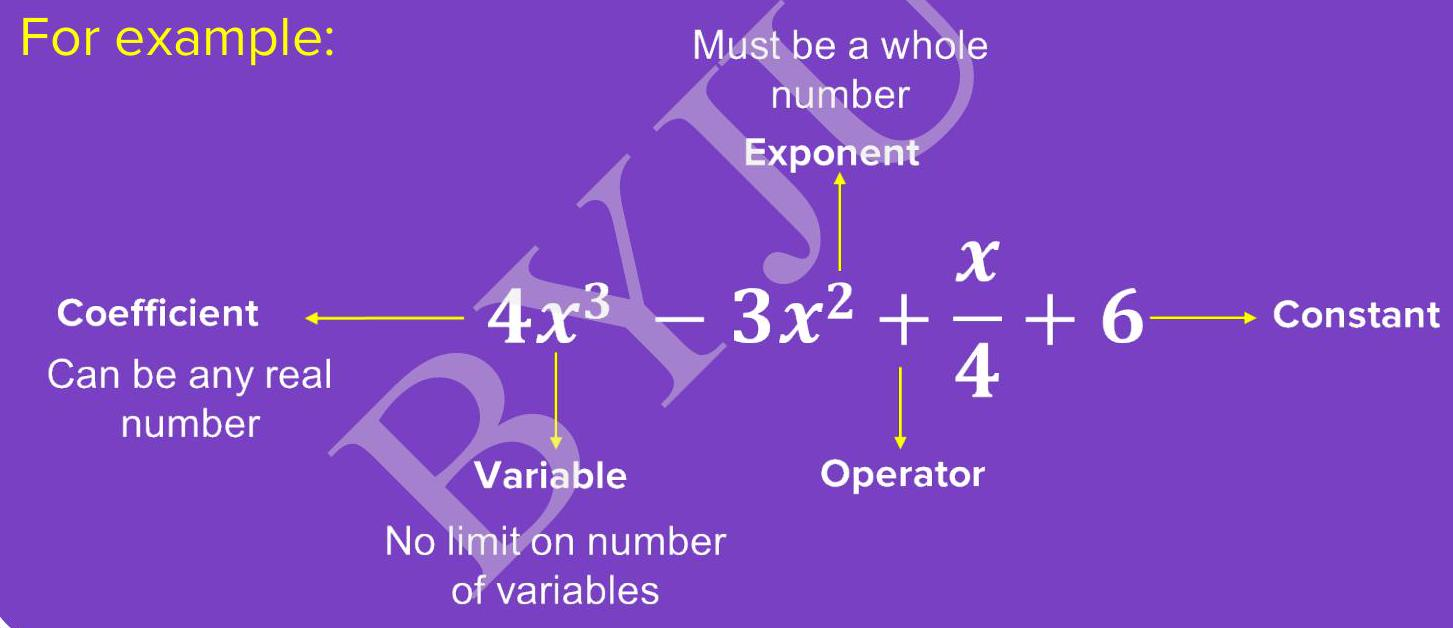
Meet the five key components
A polynomial is built from five parts. Know each name to read any expression.
Notice how each arrow points to one part. Keep these names handy—they appear often!
Key Points:
- Variable – the letter that can change, e.g., \(x\).
- Coefficient – number multiplying the variable, e.g., \(3\) in \(3x^{2}\).
- Exponent – small raised number, e.g., \(2\) in \(x^{2}\).
- Operator – plus or minus sign linking terms, e.g., \(+\) in \(3x + 5\).
- Constant – term without a variable, e.g., \(5\).
Types by Terms
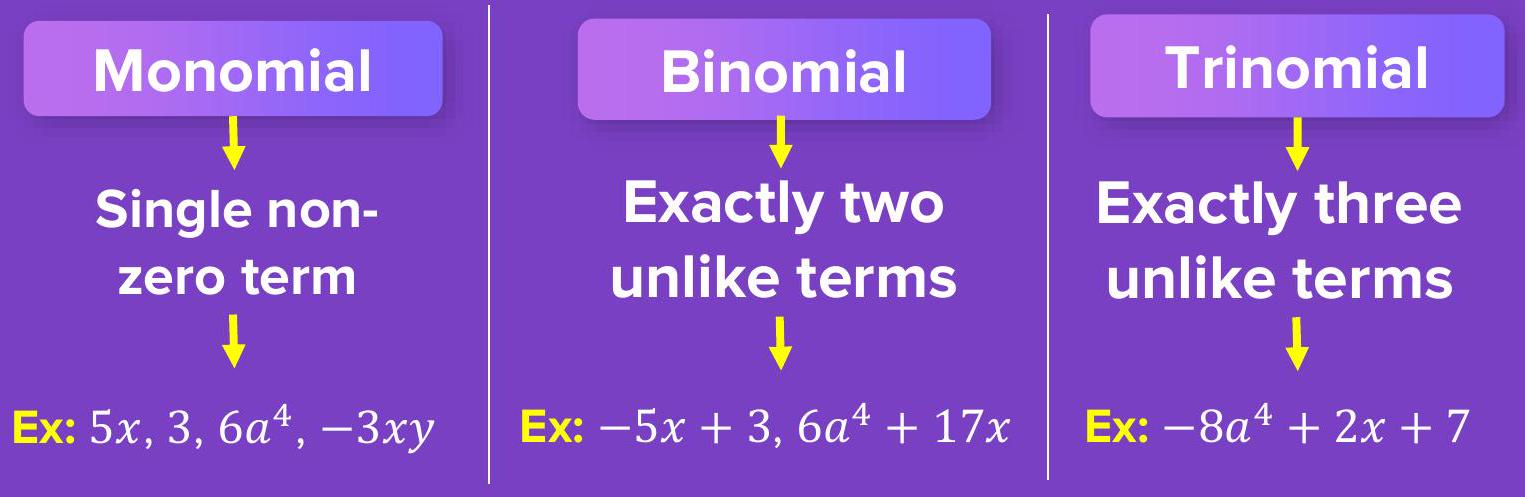
Count the unlike terms
First, split any polynomial into its unlike terms.
The number you count decides its type.
Key Points:
- Monomial – 1 unlike term
- Binomial – 2 unlike terms
- Trinomial – 3 unlike terms
Sort the Expressions!
Drag each algebraic expression into the Monomial, Binomial, or Trinomial bucket.
Draggable Items
Drop Zones
Monomial
Binomial
Trinomial
Tip:
Need a hint? Count the plus and minus signs.
Results
Degree of a Polynomial
Degree
The degree is the highest exponent of the variable. In \(3x^3 - 2x^2 + 5\), the largest exponent is \(3\); therefore, it is cubic (degree 3).
Quick check: What is the degree of \(6x^2 - x + 9\)?
Key Takeaways
Polynomial: sum or difference of terms with whole-number exponents.
Each term = coefficient × variableexponent.
By terms: monomial (1), binomial (2), trinomial (3).
Degree equals the greatest exponent present.
Next Steps
Practice more examples to cement the idea!
Thank You!
We hope you found this lesson informative and engaging.