Atomic Hypothesis
Atoms in Perpetual Motion
All matter is made of tiny particles called atoms. These atoms move continuously, attract when slightly apart, and repel when forced together.
19th-century chemist John Dalton first used this idea to explain gas laws. Quiz: choose Dalton, Maxwell, Einstein, or Feynman.
Gas Molecules in Motion
Random motion and collisions build up gas pressure.
What the image shows
Straight-line motion is interrupted by collisions; wall hits transfer momentum as tiny pushes.
- Molecular motion is random but constant.
- Collisions are elastic—speed changes, energy conserved.
- Each wall collision exerts force; many together give pressure \(P\).
- Pressure formula: \(P = \frac{F}{A}\).
Tip: Hotter gas → faster molecules → more frequent, harder hits → higher pressure.
Ideal Gas Equation
Variable Definitions
Applications
Predict Gas Behaviour
Find new pressure or volume when a tyre heats up.
Cylinder Storage Design
Calculate volume needed to store industrial gases safely.
Micro-Macro Link
Relate molecular count \(N\) to macroscopic \(P\) and \(V\).
Boyle’s Law Snapshot
Pressure × Volume = constant (temperature fixed)
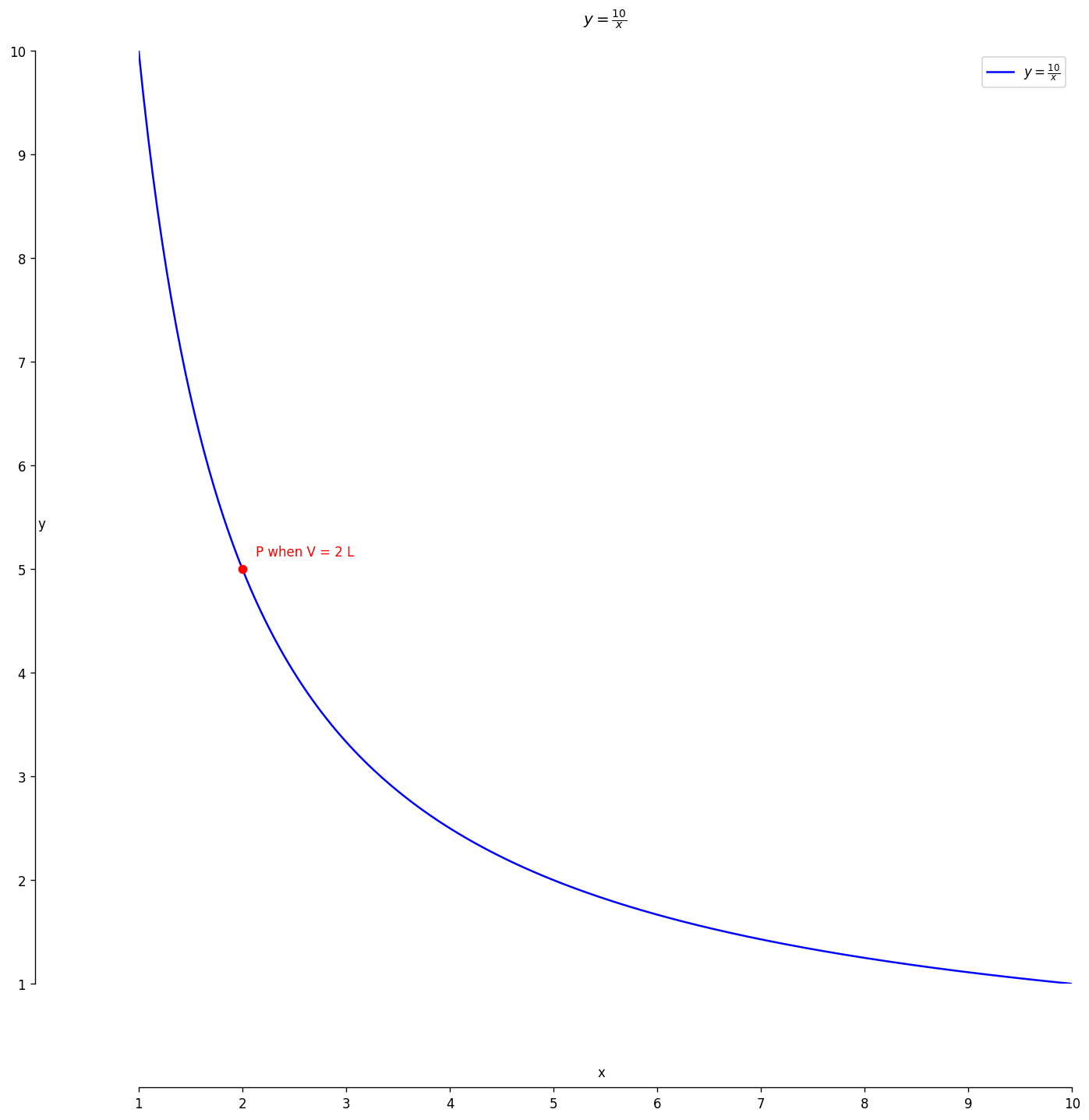
What the image shows
Keeping temperature steady, volume shrinks and pressure rises in exact inverse proportion.
- Temperature \(T\) remains constant.
- Volume ↓ ⇒ molecules hit walls more often.
- Law: \(P \propto \frac{1}{V}\) or \(PV = k\).
Tip: Double the volume and pressure halves—an easy way to spot Boyle’s Law in action.
Multiple Choice Question
Question
This concept check assesses your grasp of kinetic theory basics.
According to the kinetic theory of gases, the temperature of a gas measures the ____ of its molecules.
Hint:
Think about how fast the particles move when temperature increases.
Correct!
Yes. Temperature reflects the average kinetic energy; molecules move faster as temperature rises.
Incorrect
Remember: the term “kinetic” means motion. Temperature is linked to molecular motion, not mass or volume.
Kinetic Theory — Key Takeaways
Six bullet reminders of the theory.
Particle model
Matter consists of tiny, widely spaced particles.
Constant motion
Particles move randomly and collide elastically.
Temperature link
Average kinetic energy is proportional to \(T\): \(E_k=\tfrac{3}{2}k_B T\).
Pressure origin
Gas pressure results from particle impacts on container walls.
Absolute zero
At 0 K (−273 °C) particle motion would theoretically stop.
Gas laws
Boyle’s & Charles’s laws emerge naturally from the model.