Formal Definition
Ellipse
An ellipse is the set of all points in a plane whose distances to two fixed points, called foci, always add to the same constant value.
Which everyday objects do you think satisfy this constant-sum rule?
Focus on the Foci
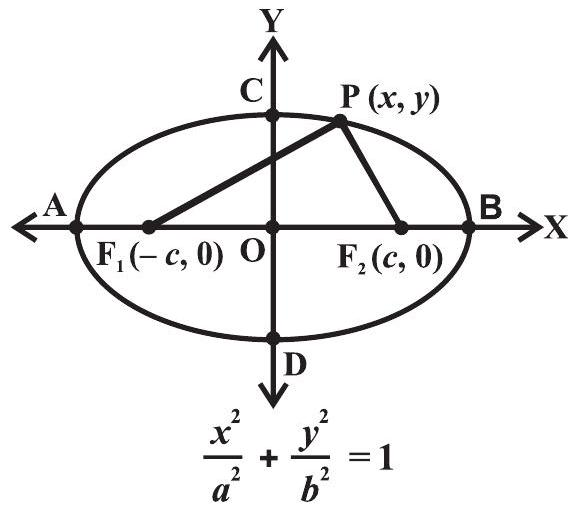
Ellipse with axes, centre and foci.
Key Parts on the Diagram
Label each part of the ellipse, then verify the focal rule.
Key Points:
- A, B: ends of the major axis, length \(2a\).
- C, D: ends of the minor axis, length \(2b\).
- \(F_1, F_2\): foci, symmetric about centre O.
- Any point \(P\) keeps \(PF_1 + PF_2 = 2a\).
The a² = b² + c² Link
Variable Definitions
Applications
Locate Foci
Use \(c=\sqrt{a^{2}-b^{2}}\) to plot focus points quickly.
Find Eccentricity
Compute \(e=\frac{c}{a}\) to measure how “stretched” the ellipse is.
Verify Ellipse Data
Check if given \(a,b,c\) satisfy the relation before graphing.
Source: NCERT Class 11 Mathematics
Two Orientations
Major Axis Along x-axis
Major Axis Along y-axis
Key Similarities
Multiple Choice Question
Question
For the ellipse \( \frac{x^{2}}{9} + \frac{y^{2}}{4} = 1 \), the point \( P(2,1) \) lies _____ the curve.
Hint:
Substitute \( x = 2, y = 1 \). Compare the sum with 1 to decide the location.
Correct!
\( \frac{4}{9}+\frac{1}{4}= \frac{25}{36} < 1 \). Therefore, \( P \) is inside the ellipse.
Incorrect
Plug the coordinates into the equation. Compare the result with 1: <1 → inside, =1 → on, >1 → outside.
Key Takeaways
Ellipses in a nutshell
Definition
Locus of points whose distances to two fixed foci add to a constant.
Standard Formulas
Centre at origin: \( \frac{x^{2}}{a^{2}}+\frac{y^{2}}{b^{2}} = 1 \); focus distance \(c\) obeys \(c^{2}=a^{2}-b^{2}\).
Orientation
If \(a>b\), major axis lies on x-axis; if \(b>a\), on y-axis; rotation introduces an \(xy\) term.
Parameter Effects
Increasing \(a\) widens, \(b\) tallens; larger \(c\) raises eccentricity \(e=c/a\).