What is a Cell?
Cell
A cell is the fundamental structural and functional unit of life—the smallest living entity able to grow, respond, reproduce and carry out metabolism independently.
Quick check: Which organism lives as a single cell yet performs all life functions? (Hint: Amoeba)
Cells Come in Many Shapes
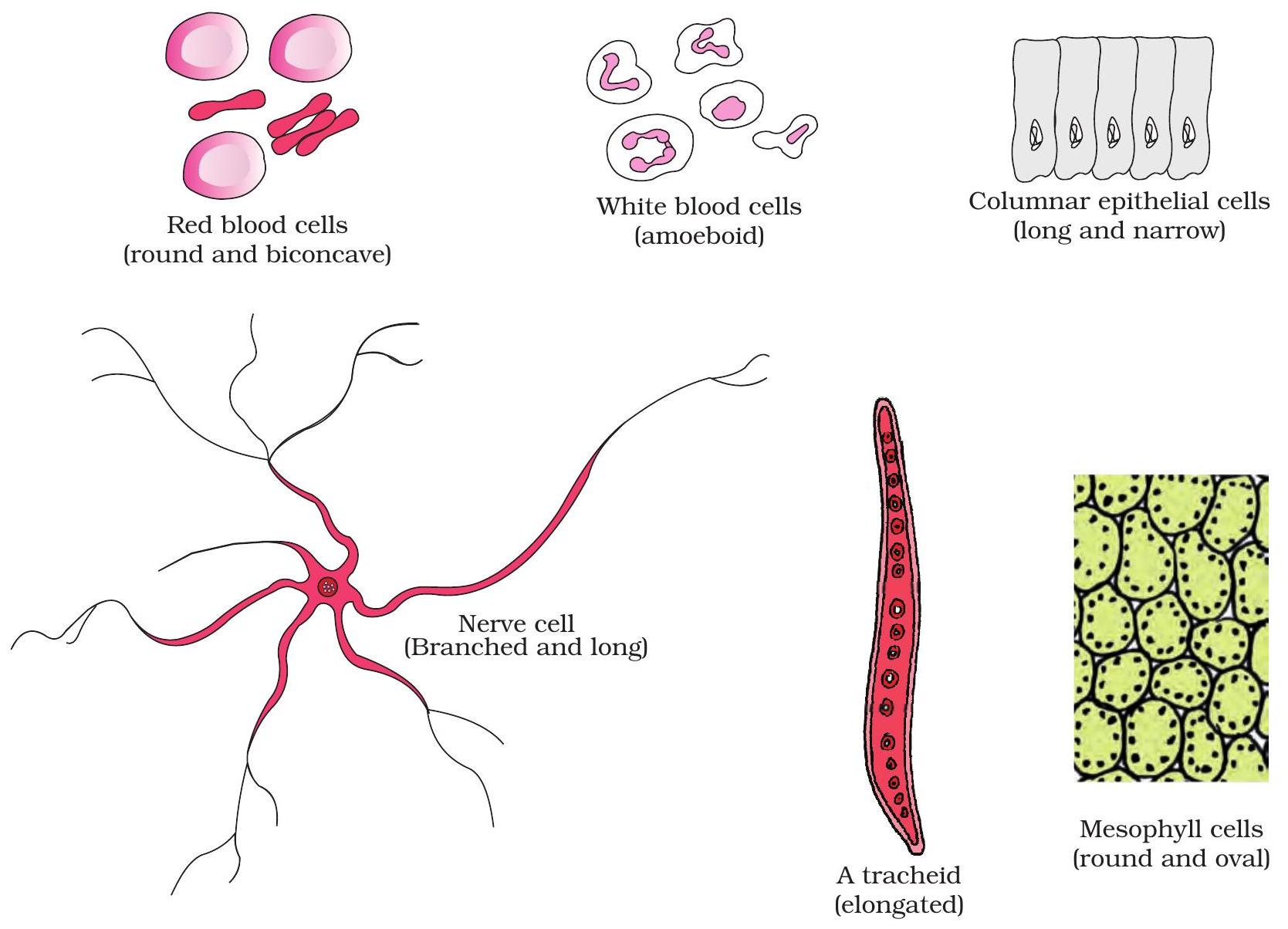
Diagram: RBC, nerve, columnar epithelium and WBC
Shape supports function
Cells vary widely. Each outline equips the cell for its task.
Spotting these forms lets us link structure to role.
Key Points:
- RBC – round, biconcave; squeezes through narrow capillaries.
- Nerve cell – long with branches; carries impulses over distance.
- Columnar cell – tall pillar; absorbs and protects linings.
- WBC – irregular, amoeboid; slips out to attack microbes.
Drag each label to its matching cell on the picture.
Birth of Cell Theory
Trace the timeline: plant cells → animal cells → cells from cells.
1838 – Matthias Schleiden
Observed that every plant organ is built from cells, launching the cell theory timeline.
1839 – Theodor Schwann
Extended the idea to animals, uniting plant and animal life under a single cellular plan.
1855 – Rudolf Virchow
Proposed “Omnis cellula e cellula” – every cell comes from a pre-existing cell, completing modern cell theory.
Pro Tip:
Remember the initials S-S-V to quickly recall the cell theory timeline.
Plant vs Animal Cell
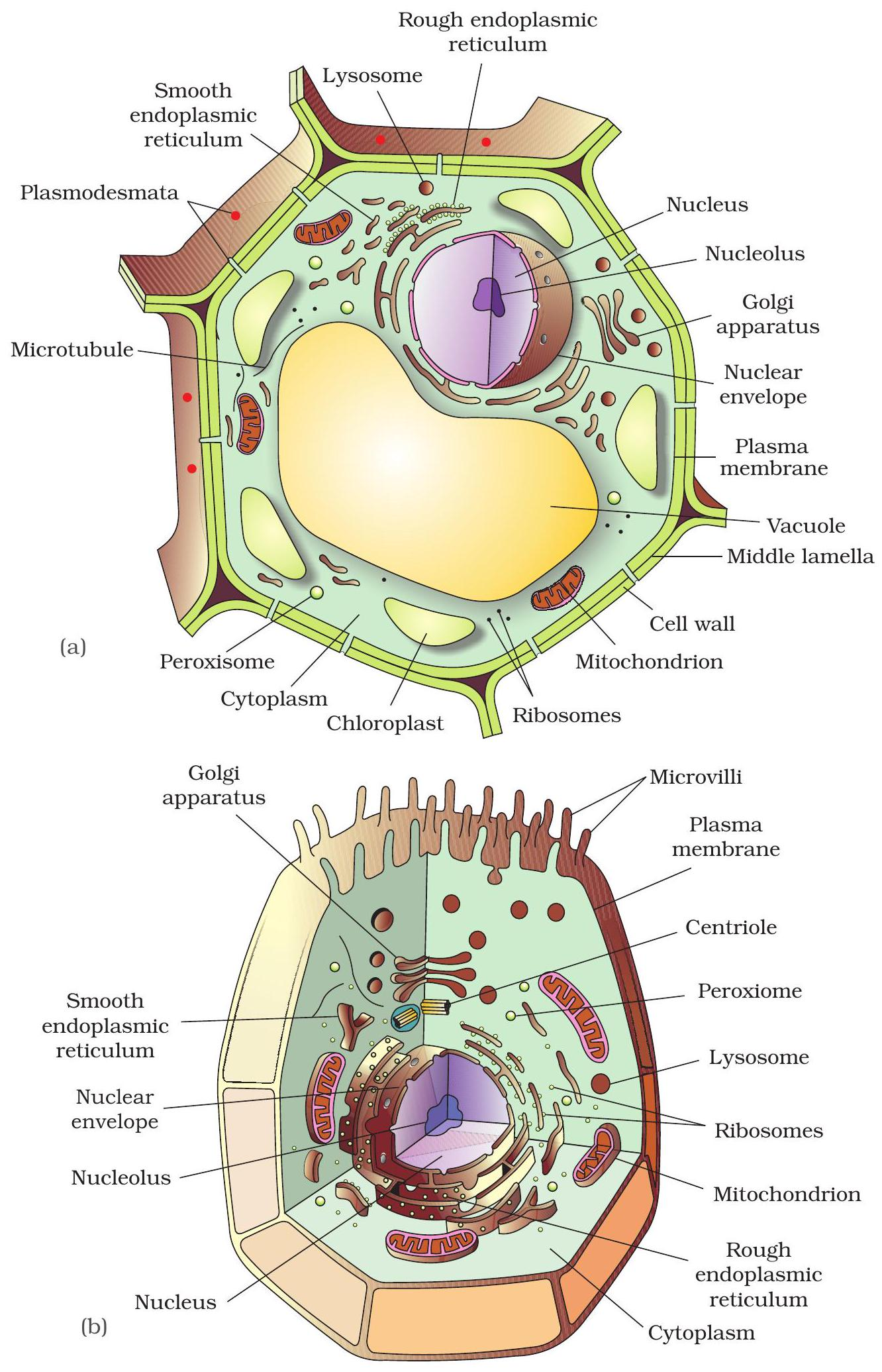
Shared & Unique Parts
Both plant and animal cells contain nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi bodies and mitochondria.
Plant cells add a rigid cell wall, large central vacuole and chloroplasts. Animal cells add centrioles and small temporary vacuoles.
Tap the chloroplast and the centriole in the diagram to test your understanding.
Key Points:
- Common: nucleus, ER, Golgi, mitochondria
- Plant-only: cell wall, chloroplast, large vacuole
- Animal-only: centriole, small vacuoles
Meet the Organelles
Main Points
- 1 Mitochondria release ATP; chloroplasts trap sunlight for glucose.
- 2 Ribosomes, rough ER and Golgi assemble, fold and ship biomolecules.
- 3 Vacuoles store materials; lysosomes and peroxisomes digest waste and toxins.
Key Highlights
-
Group by job: energy, synthesis, storage.
-
Linking structure to function sharpens memory.
-
Most textbook diagrams follow this classification.
Mitochondria: Powerhouse
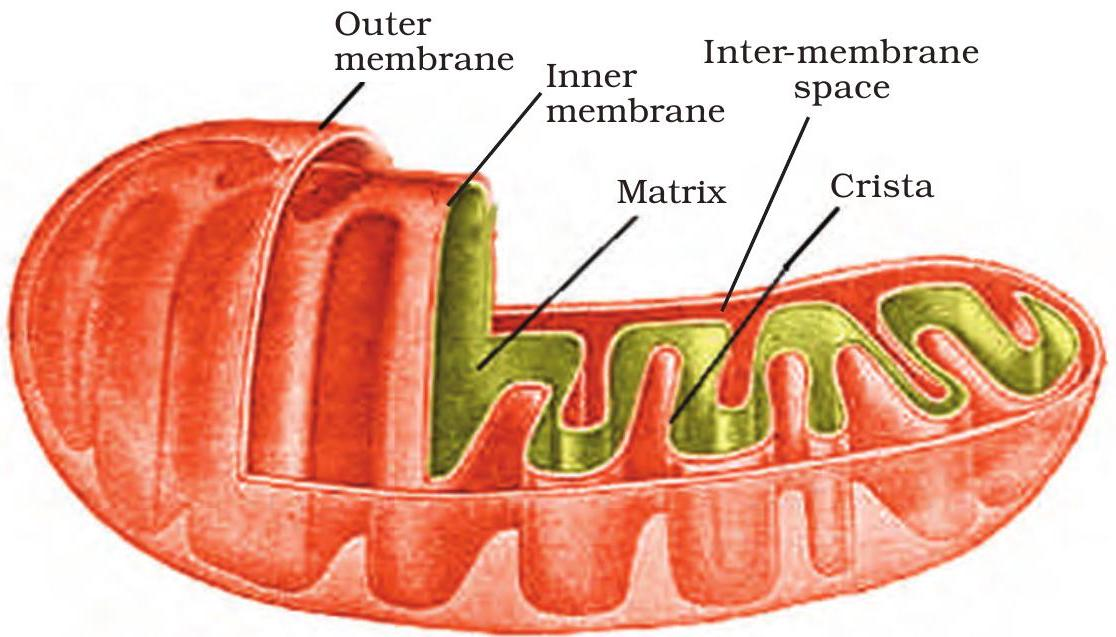
Folded cristae visible inside the double membrane.
Cristae & Matrix Fuel ATP
Mitochondrion has an outer membrane and a deeply folded inner membrane called cristae.
Cristae greatly enlarge the surface that holds the electron transport chain and ATP synthase.
The central matrix contains Krebs-cycle enzymes, circular DNA and 70 S ribosomes, allowing some protein synthesis.
Reactions on cristae and in the matrix together generate most cellular ATP.
Key Points:
- Folded cristae = larger surface → more ATP output.
- ATP synthase sits on cristae membranes.
- Matrix enzymes drive Krebs cycle and contain bacterial-like DNA & 70 S ribosomes.
Chloroplast: Green Factory
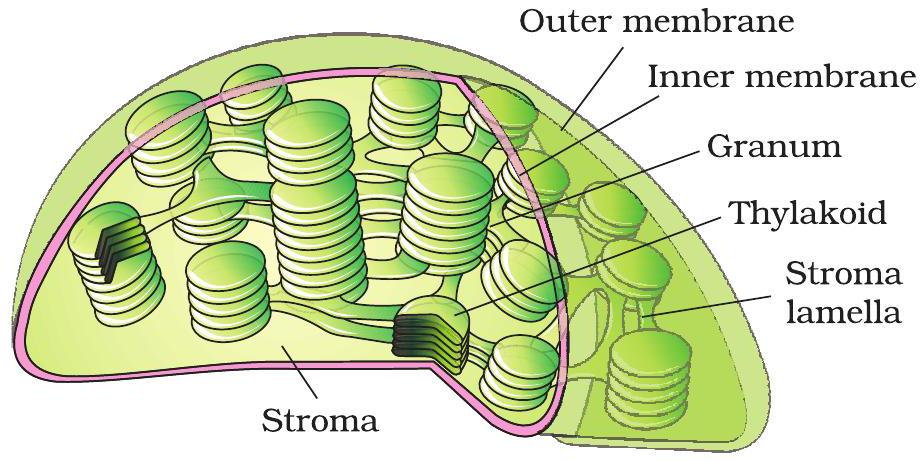
Stacks of grana inside a chloroplast
How the Parts Work Together
Chloroplasts contain flattened sacs called thylakoids, stacked into grana.
Thylakoid membranes hold chlorophyll that captures light and forms ATP + NADPH.
Energy moves into stroma, where enzymes fix CO₂ and build glucose.
Key Points:
- Light-dependent reactions occur on thylakoid membranes.
- Calvin cycle enzymes in stroma use ATP and NADPH.
- Result: sunlight + CO₂ → energy-rich sugars.
ER ➔ Golgi Highway
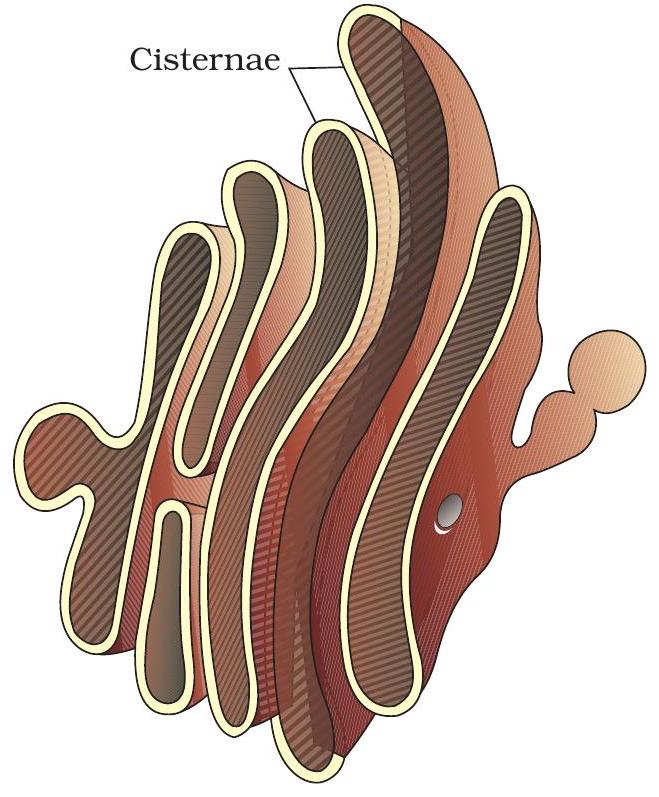
Vesicle route from Rough ER to Golgi
Protein Transit Overview
Rough ER, part of the endomembrane system, synthesises membrane and secretory proteins.
Coated vesicles bud off and move along cytoskeleton tracks to the Golgi apparatus.
The cis face receives cargo; enzymes trim, fold and tag each protein.
Finally, the trans face packages sorted proteins into vesicles for delivery or export.
Key Points:
- RER makes and folds proteins, inserts them into lumen.
- Vesicles carry cargo to Golgi cis face for modification.
- Trans face ships finished proteins — tap to confirm!
Key Takeaways
Cell = Basic Unit
Every organism is built from cells that perform all life functions.
Prokaryote vs Eukaryote
Eukaryotes have a true nucleus and organelles; prokaryotes lack both.
Membrane Systems
Plasma membrane regulates exchange; internal membranes create specialised compartments.
DNA & Ribosomes
Genetic material stores information; ribosomes translate it into essential proteins.