What Is a Circle?
Circle
A circle is the set of all points in a plane that lie at a fixed distance, called the radius, from a fixed point, called the centre.
centre → fixed point | radius → common distance
Chord vs Arc
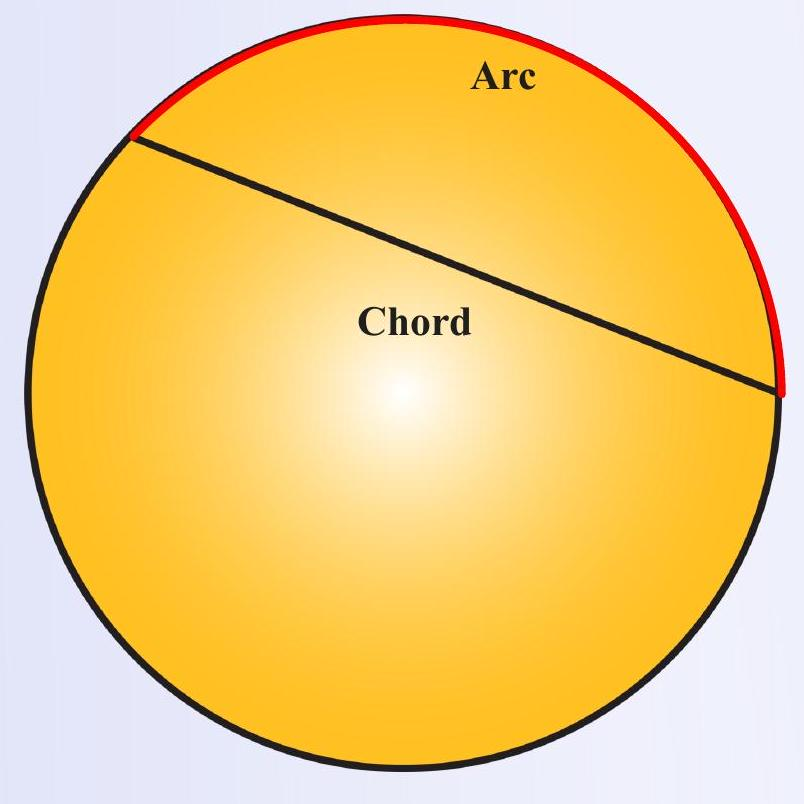
Chord (straight) and Arc (curved) joining the same endpoints
Spot the difference
A chord is a straight line segment joining two points on a circle.
An arc is the curved part of the circle’s circumference between the same two points.
Key Points:
- Chord lies inside the circle; arc lies on the circumference.
- Chord length is a straight distance; arc length follows the curve.
- Each chord defines two arcs: a minor arc (< 180°) and a major arc (> 180°).
Measuring Arc Length
Variable Definitions
Applications
Angle vs Length
Bigger \( \theta \) means a longer arc—think of cutting a larger pizza slice.
Wheel Distance
A wheel rolls distance \(s\) when it spins through \( \theta \) radians with radius \(r\).
Sector of a Circle
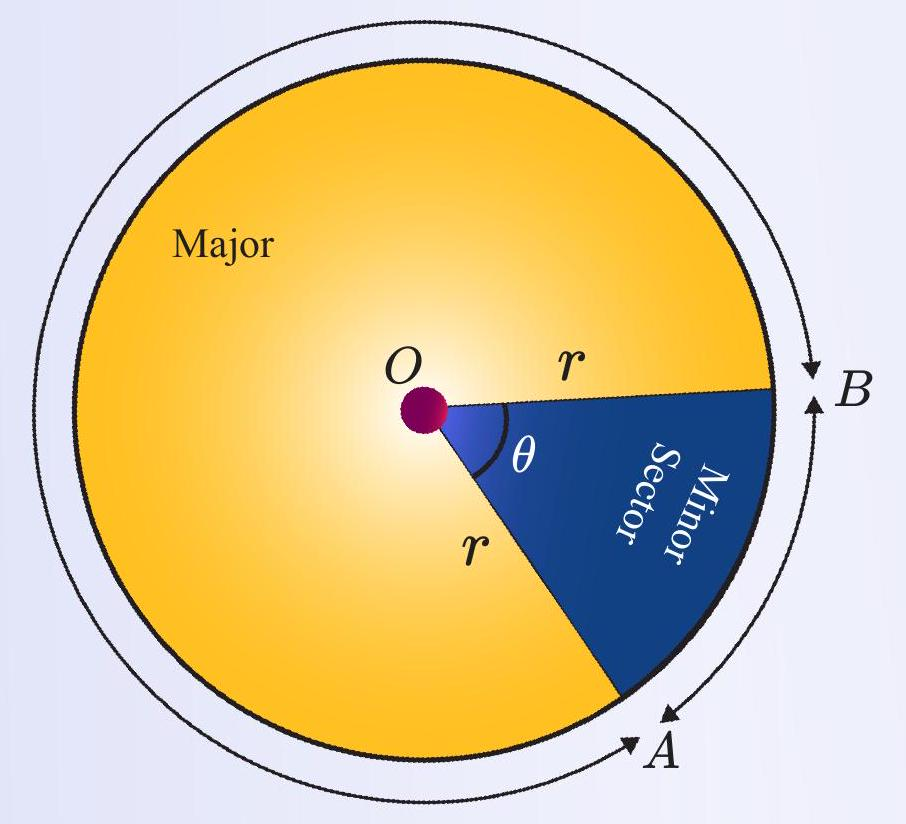
Highlighted minor sector of a circle
Definition & Everyday Picture
A sector is the region bounded by two radii and the arc between them.
Think of a pizza slice or the sweep of a speedometer needle.
Key Points:
- Minor sector: angle < \(180^\circ\) — smaller part of the circle.
- Major sector: angle > \(180^\circ\) — larger complementary part.
- Fraction relation: major sector = \(1 -\) (minor sector fraction).
Angle at Centre Rule
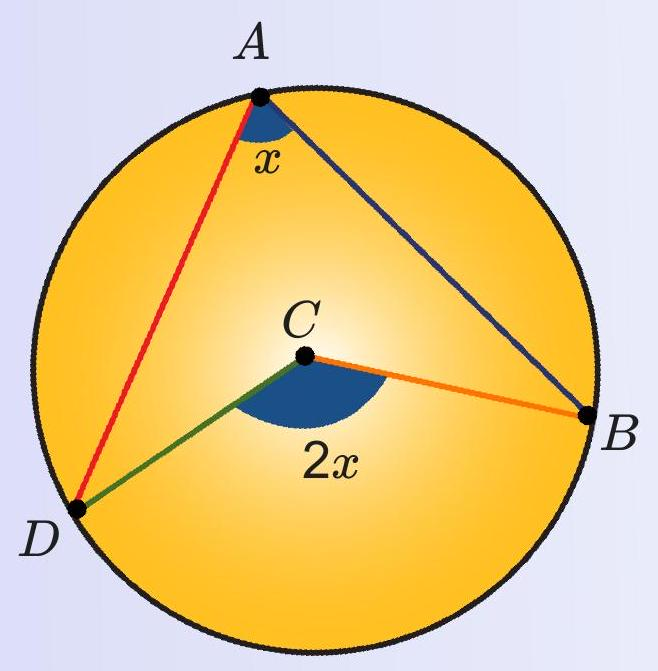
Key Theorem
For a given arc, the angle at the centre is always twice the angle at the circumference on that arc.
Example: if the circumference angle is \(30^{\circ}\), predict the central angle, then enter it in the quiz.
Key Points:
- Central angle \(= 2 \times\) circumference angle.
- Notation: \( \angle AOB = 2\,\angle ACB \) on arc \(AB\).
- Ratio 2 : 1 holds for every arc of a circle.
Key Takeaways
Circle = Locus of Points
Revision: all points \(r\) units from a fixed centre form a circle.
Chord, Arc & Sector
Revision: a chord is a straight cut, its curve is an arc, both bound a sector.
Arc Length & Central-Angle
Key idea: \( \frac{L}{2\pi r} = \frac{\theta}{360^\circ} \) links length to angle.
Next Steps
Apply these basics to tangents, cyclic quadrilaterals and angle properties next.